
Sustainability through Handloom Manufacturing

Handloom textiles are a cornerstone of sustainable fashion, offering a harmonious blend of environmental sustainability, social equity, and cultural richness. By promoting and supporting handloom products, we can foster a more diverse, ethical, and sustainable fashion industry. This shift not only benefits the environment and artisans but also enriches the fashion landscape with unique, high-quality, and meaningful garments. As consumers and stakeholders in the fashion industry increasingly prioritize sustainability, handloom textiles stand out as a beacon of responsible and beautiful fashion.
Environmental Impact
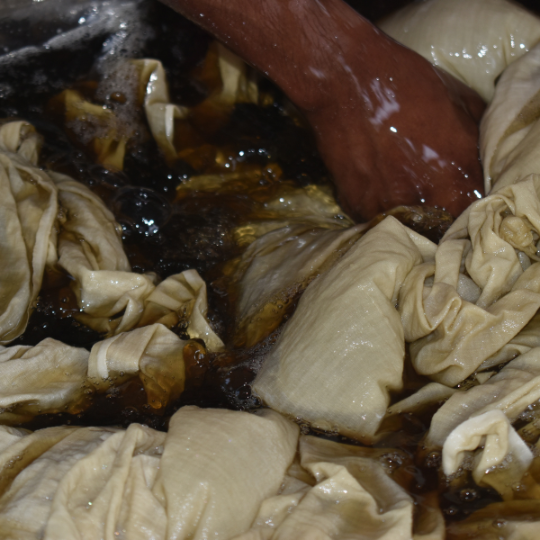

Natural Fibers and Dyes: Handloom textiles use natural fibers like cotton, wool, silk, jute and linen. These fibers are biodegradable and decompose much faster than synthetic fibers like polyester or nylon which take hundreds of years to break down.
Also natural dyes from plants, minerals and other organic materials reduce the use of chemical dyes that harm the environment and water bodies.
Lower Carbon Footprint
Lower Carbon Footprint: Handloom weaving is energy efficient. Since it’s manual labor based and not industrial machinery, it reduces the consumption of electricity and fossil fuels. This lower energy consumption translates to lower carbon footprint.
Also the decentralized nature of handloom production means less transportation of raw materials and finished products, which reduces emissions.

Economic and Social Impact
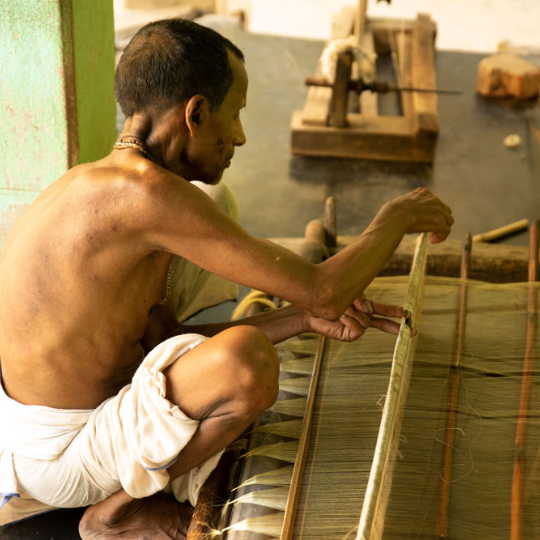

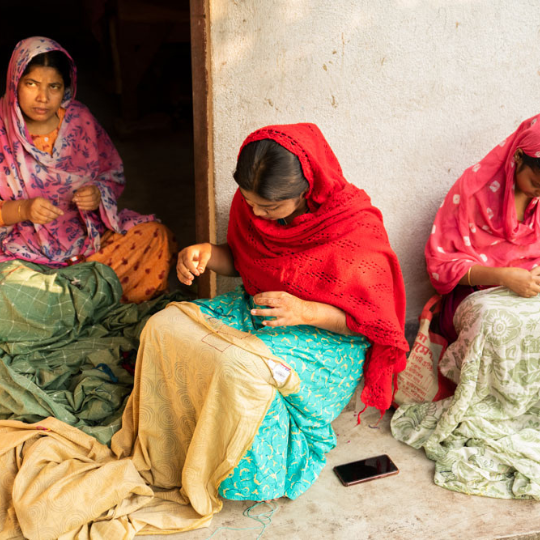
Employment and Livelihood: Handloom is a source of employment especially in rural and semi rural areas. It employs millions of artisans and provides a steady income to local economies.
The industry is often a family based enterprise, skills and knowledge is passed down through generations, thus preserving cultural heritage and providing livelihoods.
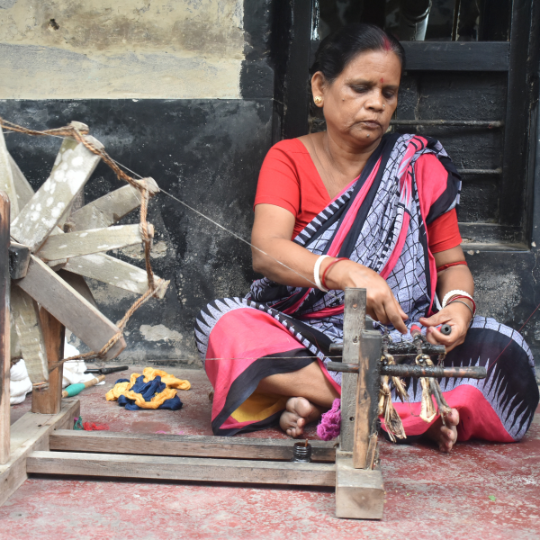
Empowerment
Empowerment: Many handloom initiatives are women led, which means financial independence and empowerment for them. This is particularly important in areas where economic opportunities for women are limited.
By weaving on handloom, women can support their families and their communities and promote gender equality and social stability.
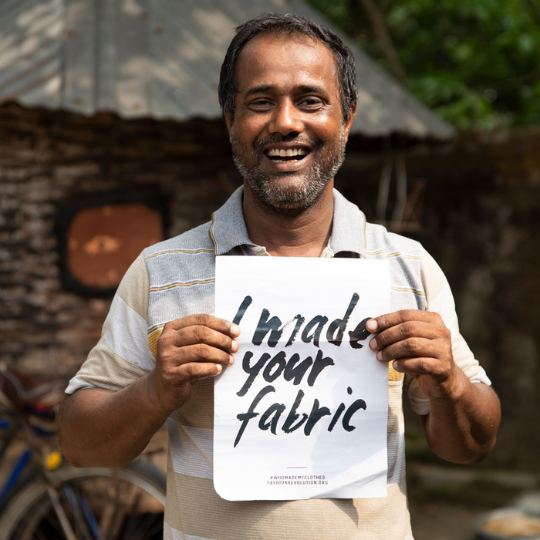

Fair Trade Practices

Fair Trade Practices: Handloom products are from cooperatives or small scale producers who follow fair trade practices. These practices ensure that artisans get fair compensation for their work, work in safe conditions and benefit from community development initiatives.
This is in contrast to the exploitative labor practices in many fast fashion supply chains.
Consumer Awareness and Trends
Slow Fashion Movement: Handloom textiles are the embodiment of the slow fashion movement. This movement is about a more mindful and sustainable approach to fashion, quality over quantity, longevity of garments and connection to the origin and makers of the clothing. Handloom textiles with its durability and timelessness fits perfectly into these values.
Challenges and Future Directions

Market Access and Competition: Despite its benefits handloom products face competition from cheaper mass produced textiles. Improving market access through online platforms, fair trade networks and collaborations with designers can help artisans reach a wider audience. Educating consumers about the environmental and social benefits of handloom can drive demand.
Innovation and Design
Innovation and Design: Mixing traditional handloom with modern design can reach a wider audience and make handloom textiles relevant in modern fashion. Designer-artisan collaborations can produce products that combines the best of both worlds – tradition and modernity.

Policy Support
Policy Support: Government support is crucial for the sustainability of the handloom sector. Policies that provide financial assistance, training, and marketing support can bolster the industry. Initiatives such as handloom fairs, exhibitions, and subsidies for raw materials can help artisans thrive. Furthermore, recognizing handloom as a vital part of cultural and economic heritage can lead to more comprehensive support measures.

related questions
What is the impact of sustainable manufacturing?
arrow_drop_downSustainable manufacturing reduces environmental impact, conserves resources, and minimizes waste. It enhances energy efficiency, ensures ethical labor practices, and supports long-term ecological balance, benefiting both communities and economies by promoting overall well-being and resilience.
What does sustainability mean in textiles?
arrow_drop_downIn textiles, sustainability means using eco-friendly materials, reducing waste, conserving resources, and ensuring ethical labor practices. It focuses on creating durable products with minimal environmental impact, promoting recycling, and supporting fair trade and responsible manufacturing processes.
What is the most sustainable textile material?
arrow_drop_downOrganic cotton is often considered the most sustainable textile material. It's grown without harmful pesticides, uses less water, and supports biodiversity. Other sustainable options include hemp, linen, and bamboo, which are eco-friendly and have a lower environmental impact.
Why is sustainability important in the textile industry?
arrow_drop_downSustainability in the textile industry is crucial to reduce environmental pollution, conserve resources, and minimize waste. It ensures ethical labor practices, promotes biodiversity, and supports long-term ecological balance, benefiting both the planet and future generations.
More Blogs

navigating the logistics of fabrics wholesale: a guide to indian bulk textile export

khaadi online shopping guide: khaadi vs organic linen for sustainable summer fashion

navigating fabrics wholesale: a comprehensive guide to moqs and sampling protocols for sustainable brands

a strategic guide to sourcing fabrics wholesale in india for global brands

ethical supply chains: the sustainability impact of khaadi online shopping

performance metrics: analyzing banana fiber fabric properties for textile design






