
Trash To Treasure: Vermicomposting

In a world grappling with the consequences of excessive waste production, especially from textile waste and fast fashion, vermicomposting emerges as an unlikely hero for many ecosystems. Earthworms innate ability to recycle organic waste, including textile waste, through vermicomposting offers a sustainable, environmentally friendly solution to the global garbage crisis. By harnessing the power of these unsung champions, we can reduce landfill waste, enrich our soils, and pave the way for a cleaner, greener future.
Anuprerna, as an advocate for sustainability in the textile industry, recognizes the importance of addressing waste management issues. By promoting practices such as vermicomposting, Anuprerna aims to reduce environmental impact and pave the way for a cleaner, greener future.
The Garbage Crisis: A Growing Concern

The world's garbage crisis is reaching alarming proportions. With landfills overflowing, plastic pollution devastating ecosystems, and greenhouse gas emissions from decomposing waste contributing to climate change, urgent action is imperative. Traditional solid waste management methods are no longer sufficient to address this crisis effectively.
Escalating Waste Volumes
The sheer volume of waste generated globally is staggering. Each year, billions of tons of waste end up in landfills, contributing to soil and water pollution along with other environmental issues. It's a critical problem that demands immediate attention.
Plastic Pollution
The proliferation of single-use plastics has added another layer to the garbage crisis. These non-biodegradable materials persist in the environment for centuries, causing harm to wildlife and ecosystems.
Earthworms: Nature's Recycling Machines
Earthworm Anatomy
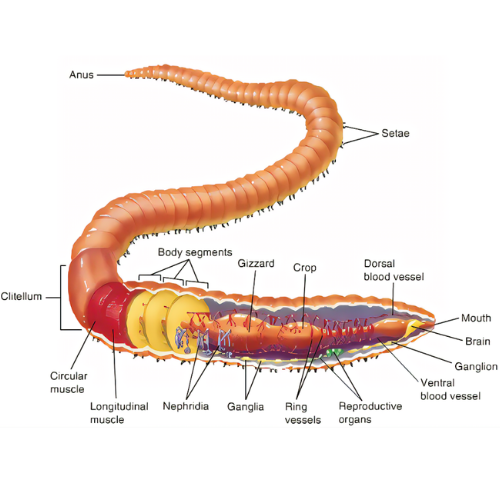
To truly appreciate the role of earthworms in waste management, let's delve deeper into their unique biology. Earthworms are segmented invertebrates with a tubular body divided into several segments. Their body structure facilitates locomotion through soil, and their specific features make them ideal candidates for waste decomposition and recycling.
Segmental Structure
The segmentation of an earthworm's body allows for flexibility and movement. Each segment contains muscle fibres and bristles, enabling them to burrow through soil efficiently.
The Digestive Process
Earthworms possess a specialized digestive system that enables them to consume and break down organic matter efficiently. Their diet primarily consists of decomposing leaves, dead plants, and other organic materials. As they ingest organic waste, earthworms produce nutrient-rich excrement, known as castings, which enhances soil fertility.
Gizzard and Crop
Earthworms have a unique two-part digestive system comprising a muscular gizzard and a crop. The gizzard grinds down ingested organic matter, while the crop temporarily stores it, facilitating gradual digestion.
Soil Aeration
Besides their digestive prowess, earthworms play a crucial role in soil aeration. Their burrowing activities create channels in the soil, allowing for improved water infiltration and the exchange of gases. This not only benefits plant growth but also aids in the breakdown of organic solid waste within the soil.
The Burrowing Process
Earthworms burrow by expanding and contracting their bodies. This burrowing action helps in mixing organic matter with the soil, promoting decomposition and nutrient cycling.
Earthworms in Waste Management: Vermicomposting

One of the most cost-effective ways to utilize earthworms for waste management is through vermicomposting. This process involves the controlled decomposition of organic waste using earthworms. Here's how it works:
Collection of Organic Waste
Start by collecting kitchen scraps, garden waste, and other organic or textile materials. Anything from fruit and vegetable peels to coffee grounds can be used.
Creating a Vermicompost Bin
Construct or purchase a suitable vermicompost bin with adequate ventilation. This ensures a healthy environment for your earthworms.
Adding Earthworms
Introduce a population of earthworms into the bin. Red wigglers (Eisenia fetida) are commonly used for this purpose due to their voracious appetite and efficient composting abilities.
Feeding the Worms
Regularly add organic waste to the bin, ensuring a balanced diet for the worms. Avoid overfeeding, as it can lead to issues such as odor and poor compost quality.
Harvesting Vermicompost
Over time, the earthworms will transform the organic matter into nutrient-rich vermicompost. Harvest this black gold to fertilize gardens and reduce the need for chemical fertilizers.
Advantages of Vermicomposting

Vermicomposting offers a multitude of benefits, making it an eco-friendly and sustainable solid waste management solution:
Volume Reduction: Vermicomposting significantly reduces the volume of organic waste that ends up in landfills, helping to alleviate the burden on already overcrowded waste disposal sites.
Nutrient-Rich Compost: The vermicompost produced is of high quality, rich in essential nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. It enhances soil fertility, promoting healthier plant growth.
Cost-Effective and Sustainable: This process is not only environmentally friendly but also cost-effective in the long run. It reduces the need for chemical fertilizers, saving both money and resources.
The Global Impact
Earthworm-based solid waste management practices extend far beyond local gardens and farms. They have the potential to address the global garbage crisis in several ways also helping the handloom and textiles industry be more sustainable
Reducing Landfill Pressure
By diverting organic waste from landfills, vermicomposting reduces the burden on already overcrowded waste disposal sites. This, in turn, decreases the release of harmful greenhouse gases associated with landfill decomposition, contributing to a reduction in global carbon emissions. Sustainable clothing produced from handloom fabrics also helps earthworms in easier vermicomposting
Promoting Sustainable Agriculture and Textile Production
Vermicompost serves as an excellent organic fertilizer, improving crop yields and soil health. Widespread adoption of this natural fertilizer could contribute to sustainable agricultural and textile practices, reducing the need for chemical inputs and promoting environmentally friendly farming and handloom weavers in producing sustainable handloom products
Meet the Plastic Eating Worms

related questions
What is the vermicomposting process?
arrow_drop_downVermicomposting is a process of composting organic waste using worms, which consume the waste and turn it into nutrient-rich compost.
What are the benefits of vermicomposting?
arrow_drop_downThe benefits of vermicomposting include nutrient-rich compost, improved soil structure, waste reduction, cost-effectiveness, sustainability, and ease of management.
What is the role of earthworm in vermicomposting?
arrow_drop_downThe role of earthworms in vermicomposting is to consume organic waste materials, break them down through digestion, and produce nutrient-rich compost known as vermicompost or worm castings.
What type of waste is used in vermicomposting?
arrow_drop_downVarious types of organic waste, such as fruit and vegetable scraps, coffee grounds, shredded paper, yard trimmings, and plant-based kitchen waste, are used in vermicomposting.
More Blogs

navigating the logistics of fabrics wholesale: a guide to indian bulk textile export

khaadi online shopping guide: khaadi vs organic linen for sustainable summer fashion

navigating fabrics wholesale: a comprehensive guide to moqs and sampling protocols for sustainable brands

a strategic guide to sourcing fabrics wholesale in india for global brands

ethical supply chains: the sustainability impact of khaadi online shopping

performance metrics: analyzing banana fiber fabric properties for textile design






