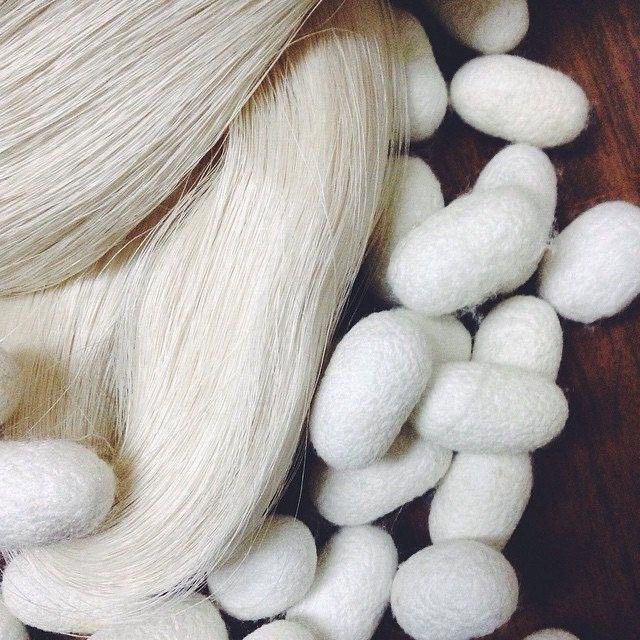

The Evolution of Silk Production: A Journey Towards Sustainability

Silk, renowned for its luxurious texture and shimmering appearance, has been a prized fabric for centuries. However, traditional silk production has raised environmental and ethical concerns, prompting a shift towards more sustainable practices searching for more sustainable fabrics including sustainable silk.
Introduction
The need for sustainable silk arises from environmental and ethical concerns surrounding traditional silk production and the production artificial silk. Artificial, non-sustainable silk such as nylon, rayon is increasingly replacing natural silk due to its lower cost, durability, and versatility in design. This shift impacts traditional silk-producing economies and ecosystems reliant on silk production. While synthetic silk reduces reliance on natural resources like silkworms, its production involves chemicals and energy-intensive processes, contributing to environmental concerns such as pollution and resource depletion. The trend highlights a trade-off between economic benefits and sustainability, prompting concerns over the long-term ecological impacts and the need for more sustainable alternatives in textile manufacturing.
The Role of Indian Silk Industry

The Indian silk industry is integral to the country's economy, creating millions of employment opportunities in sericulture, weaving, and garment production. Renowned for its diverse silk varieties like Tussar, Muga, and Mulberry, India ranks among the world's top silk producers. The industry fosters cultural heritage and trade, particularly in states like Karnataka, West Bengal, and Assam. Today, silk industry is at a crossroads, with growing demand for sustainable silk .This demands sparks big shifts. Top fashion names now use more of sustainable silk. This trend pushes new ideas and money into eco-friendly silk farming methods.
The legacy of Indian Silk Industry
Indian silk is celebrated globally for its rich diversity and exquisite craftsmanship. Varieties like Mulberry, Tussar, and Muga are prized for their luxurious texture, vibrant colors, and intricate weaving techniques. The country's silk industry combines traditional knowledge with modern innovation, producing high-quality fabrics that cater to diverse aesthetic preferences. Indian silk's reputation stems from centuries of skilled craftsmanship and its role in cultural ceremonies, fashion, and luxury markets worldwide.

Production Process of Silk

Silk production begins with sericulture, where silkworms are reared on mulberry leaves. Once matured, silkworms spin cocoons made of silk threads. These cocoons are harvested and boiled to soften the sericin protein that holds the threads together. The softened threads are then unwound from the cocoon, spun together, and woven into fabric. Traditional methods involve boiling the cocoons with chemicals, while sustainable practices aim to minimize environmental impact through organic farming, natural dyes, and humane silk extraction methods like peace silk.
The Rise of Peace Silk
Peace silk, also known as Ahimsa silk, represents a significant ethical advancement in the silk industry. Unlike traditional methods, peace silk production allows the silkworms to complete their lifecycle and emerge from their cocoons naturally. The silk is then spun from the empty cocoons, ensuring no harm to the insects. These are few benefits of peace silk.
- Animal Welfare: Peace silk is cruelty-free, aligning with the values of consumers who prioritize animal welfare.
- Sustainable Fabric: By allowing silkworms to live out their natural lifecycle, peace silk production reduces the ecological impact associated with traditional sericulture.
- High-Quality Fabric: Peace silk maintains the luxurious qualities of traditional silk, offering a sustainable fabric option without compromising on quality.

Summary
Sustainable practices aim to minimize environmental impact by reducing water use, pesticide use, and carbon emissions. Ethical considerations include ensuring fair labor practices and animal welfare. By promoting sustainable silk process, we support biodiversity, conserve resources, and foster a more ethical industry that respects both people and the planet.
related questions
What impact does silk have on the world today?
arrow_drop_downSilk remains vital today, influencing fashion, luxury markets, and traditional crafts. Its sustainable and biodegradable nature contributes positively to the environment, while its production supports economies in Asia, preserving cultural heritage and providing livelihoods.
How to make silk sustainable?
arrow_drop_downMaking silk sustainable involves using organic farming methods, ensuring ethical labor practices, reducing water and chemical usage, promoting fair trade, and supporting wild silk production, which conserves biodiversity and minimizes environmental impact.
Can silk be recycled?
arrow_drop_downYes, silk can be recycled. Old silk garments and fabrics can be reprocessed into new fibers or repurposed for different uses, reducing waste and promoting sustainability in the fashion industry.
Is silk Environmentally friendly?
arrow_drop_downSilk is relatively environmentally friendly due to its natural biodegradability and low energy production. However, its environmental impact can be improved by adopting organic farming practices, reducing chemical use, and ensuring sustainable and ethical production methods.
Can silk be made without killing silkworms?
arrow_drop_downYes, silk can be made without killing silkworms through methods like peace silk or Ahimsa silk production, where silkworms are allowed to emerge naturally from their cocoons before the silk is harvested, ensuring a cruelty-free process.
More Blogs

screen printing on natural fabrics: what experience teaches that manuals don’t

understanding mulberry silk quality: what designers often miss and why it matters

bengal looms for men: beyond the kurta
jamdani magic: why this weave is unesco-recognized as cultural heritage

weaving geography: which district is known for which handloom fabrics

the ultimate guide to naturally dyed and block printing textiles






